Magnolia berry protects against acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity
01/03/2019 / By Michelle Simmons
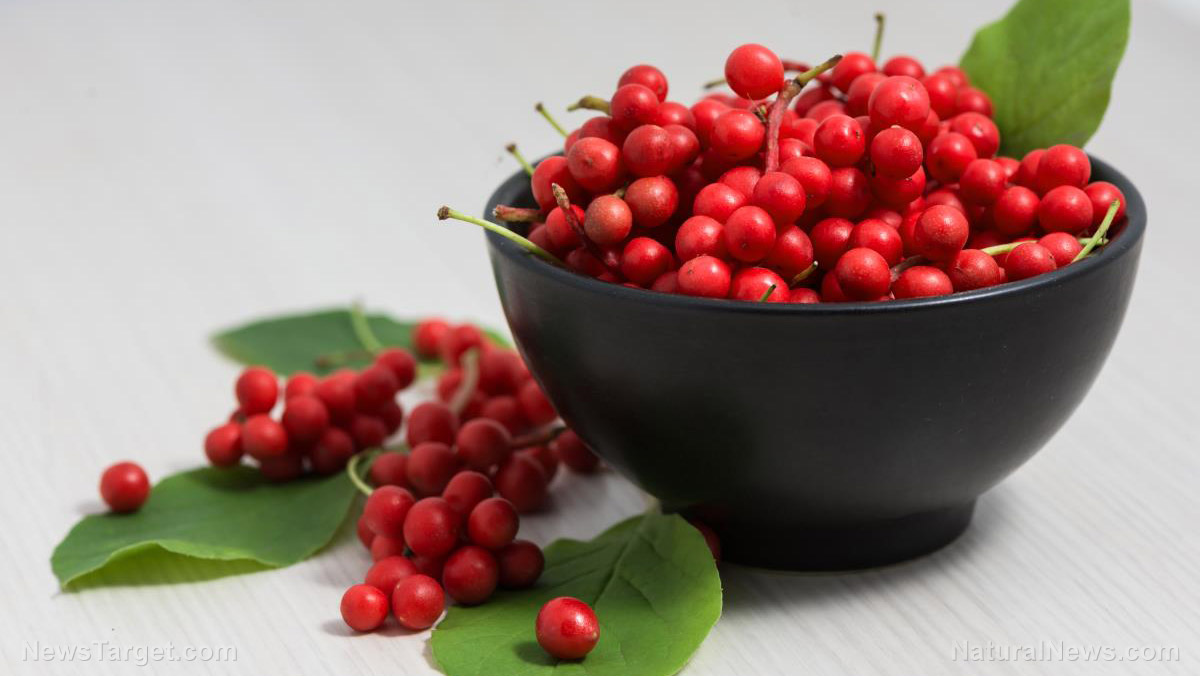

Researchers at Jilin Agricultural University and Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences (CAAS) in China discovered that magnolia berry (Schisandra chinensis) possesses protective effects against liver damage caused by acetaminophen. In their study, which was published in the Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines, they focused on evaluating the effects of an ethanol extract of magnolia berry stems on acetaminophen-induced liver damage in an animal model.
- For the study, the researchers gave mice an ethanol extract of magnolia berry stems for seven consecutive days.
- Then, they administered acetaminophen in mice to cause liver damage.
- They also analyzed the compounds in magnolia berry extract and found that it contains chisandrol A, schisandrol B, deoxyschisandrin, schisandrin B, and schisandrin C.
- Results of the stem extract pretreatment showed that magnolia berry ameliorated liver dysfunction and oxidative stress in mice.
- This was seen through the significant reductions in aspartate transaminase (AST), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), and malondialdehyde (MDA) contents and increases in reduced glutathione (GSH) and superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels.
- The pretreatment also significantly reduced expression levels of 4-hydroxynonenal (4-HNE) and 3-nitrotyrosine (3-NT).
- It also significantly reduced the expression levels of Bax, mitogen- activated protein kinase (MAPK), and cleaved caspase-3 by acetaminophen exposure.
- In addition, magnolia berry stem extract reduced inflammatory response by suppressing the expression levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2).
- These results suggest that magnolia berry stem extract exhibited significant reductions in oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis primarily by regulating MAPK and caspase-3 signaling pathways.
In conclusion, this study shows that magnolia berry may help protect against liver damage caused by acetaminophen.
To read more studies on natural medicines for liver damage, visit LiverDamage.news.
Journal Reference:
Li YZ, Ma ZN, Sun YS, Ren S, Jiang S, Zhang WZ, Wang Z, Li W. PROTECTIVE EFFECTS OF EXTRACTS OF SCHISANDRA CHINENSIS STEMS AGAINST ACETAMINOPHEN-INDUCED HEPATOTOXICITY VIA REGULATION OF MAPK AND CASPASE-3 SIGNALING PATHWAYS. Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines. 2018; 16(9): 700-713. DOI: 10.1016/S1875-5364(18)30110-9
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
Acetaminophen, alternative medicine, anti-apoptosis, anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation, antioxidants, five-flavor berry, hepatotoxicity, herbal medicine, Herbs, Liver, liver damage, liver health, magnolia berry, medicinal plants, natural cures, natural healing, natural medicine, natural remedies, Schisandra chinensis
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author