Evaluation of xiao yao san’s anti-anxiety activities
01/26/2021 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez
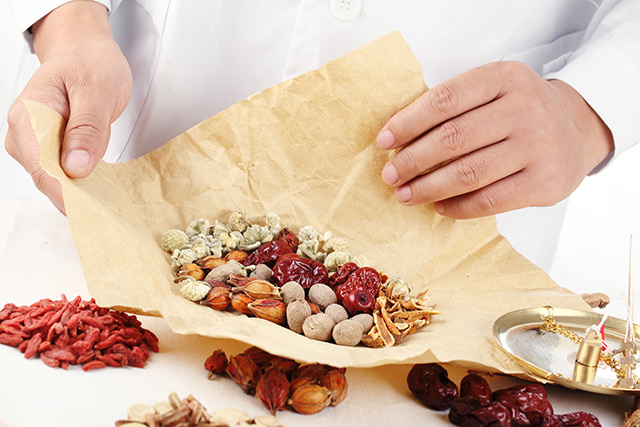

Researchers at Beijing University of Chinese Medicine evaluated the effects of xiao yao san (XYS) on anxiety-like behaviors and the mechanisms underlying its activity. They reported their findings in an article published in the journal Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.
- The researchers wanted to explore whether the c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) signaling pathway, which is involved in regulating many key cellular processes, is also involved in XYS’ effects.
- They divided 40 rats into 5 groups:
- The control group, which received deionized water
- The model group, which also received deionized water
- The SP600125 group, which underwent surgery
- The per se group, which also underwent surgery
- The XYS group, which received 3.9 g/kg XYS daily
- They injected a 1 percent dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) citrate buffer solution and SP600125 separately and bilaterally into the rats (via the brain’s ventricular system) in the two surgery groups.
- They then subjected all the groups except for the control to 14 days of chronic immobilization stress (CIS).
- On day 15, the researchers measured the body weight of the rats and subjected the animals to the elevated plus maze (EPM) and novelty suppressed feeding (NSF) tests.
- They then examined JNK signaling pathway indices, including phosphorylated JNK (P-JNK), JNK, phosphorylated c-Jun (P-c-Jun) and cytochrome C (Cyt-C).
- Based on the body weight and behavioral analyses of the model rats, the researchers confirmed the successful induction of anxiety-like behaviors in the animals.
- They reported that P-JNK, JNK and P-c-Jun expression was altered in the hippocampus of the model rats.
- Treatment with XYS and SP600125 for 14 days changed rat body weight and behaviors, along with P-JNK, JNK and P-c-Jun expression levels, for the better.
- However, the treatments had no effect on Cyt-C.
These results suggest that XYS reduces anxiety-like behaviors induced by CIS, which might be related to the JNK signaling pathway in the hippocampus.
Journal Reference:
Zhao HB, Jiang YM, Li XJ, Liu YY, Bai XH, Li N, Chen JX, Liu Q, Yan ZY, Zhao FZ. XIAO YAO SAN IMPROVES THE ANXIETY-LIKE BEHAVIORS OF RATS INDUCED BY CHRONIC IMMOBILIZATION STRESS: THE INVOLVEMENT OF THE JNK SIGNALING PATHWAY IN THE HIPPOCAMPUS. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin. 01 February 2017;40(2):187–194. DOI: 10.1248/bpb.b16-00694
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anxiety relief, Chinese medicine, herbal medicine, Herbs, mental health, natural cures, natural medicine, remedies, research, xiao yao san