Lifestyle factors that reduce the risk of developing IBD
09/21/2025 / By Willow Tohi

- Study finds adhering to healthy lifestyle practices can significantly decrease the chance of developing inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
- The study clarifies the types and symptoms of IBD, explaining what it means to live with this condition.
- The study outlines key habits, from diet to physical activity, that can help prevent IBD.
- The study details diets and supplements that may aid in managing IBD, and explores non-traditional treatments like stress management, sleep and hydration.
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), which encompasses Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis, is a chronic, debilitating condition characterized by long-term inflammation in the digestive tract. A recent study found that adopting certain healthy lifestyle habits can dramatically reduce the risk of developing IBD by as much as 61%. This groundbreaking research, based on the data from over 200,000 adults in the United States and Europe, highlights the role of nutrition, physical activity, and the avoidance of harmful habits like smoking in preventing IBD. Now, more than ever, understanding these factors can empower individuals to take proactive steps in managing their health.
Nutritional approaches for managing IBD: Adapting to a healthier diet
One of the most significant findings from the study was the impact of diet on the prevention of IBD. The research emphasized the importance of increasing the intake of fruits, vegetables, and dietary fiber while reducing factory-farmed protein consumption. Whole foods rich in antioxidants and phytochemicals can enhance gut health and reduce inflammation. Incorporating fiber sources such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support the gut microbiome and maintain a balanced intestinal environment. This aligns with the notion that nutrition plays a crucial role in how it interacts with your body, enabling you to manage IBD effectively.
Physical activity to support gut health
Physical activity is another key component highlighted in the study. Engaging in regular exercise not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also promotes gut health and reduces stress. Research has demonstrated that regular physical activity can mitigate the severity of symptoms related to autoimmune diseases, including IBD, by decreasing fatigue and improving mood. This underscores the importance of adopting an active lifestyle to support overall health and well-being.
Avoiding harmful substances
The study also underlined the dangers associated with high body mass index (BMI) and smoking, both of which are linked with an increased risk of IBD. Furthermore, over-reliance on certain over-the-counter pain relievers like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can adversely affect the gut microbiome, leading to inflammation and other complications. By incorporating regular exercise and avoiding such harmful substances, individuals can take control of their health and reduce the risk of developing IBD.
Dietary adjustments
For those already diagnosed with IBD, the study also provides insights into dietary adjustments that can help manage the condition. The study recommends the IBD-AID plan, a structured approach that begins with an introduction to basic, anti-inflammatory foods before gradually reintroducing more nutritious and varied meals. Key components of the IBD-AID plan include smoothies, oatmeal, pureed fruits and vegetables, lean meats, and flax or chia seeds. Gradually, more complex fibers and nutrients are introduced to support digestion and maintain remission. Additionally, adhering to a low-FODMAP diet can help manage symptoms by eliminating specific sugars that are difficult to digest.
Supplements and herbs
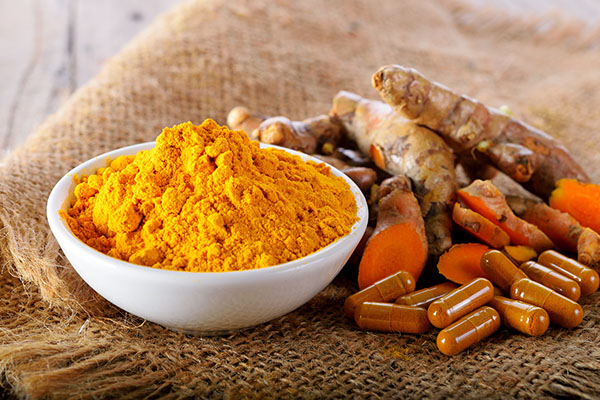
Complementary treatments such as curcumin, Qing Dai and Boswellia Serrata also show promise in managing IBD symptoms. Curcumin, derived from turmeric, has been recognized for its anti-inflammatory properties, while Qing Dai and Boswellia Serrata offer targeted antioxidant benefits. These supplements can help strengthen gut integrity, promote the growth of beneficial bacteria, and reduce overall inflammation.
Holistic health for IBD goes beyond diet and exercise: Managing stress and mental health
The brain-gut connection, often referred to as the HPA axis, plays a significant role in IBD management. Chronic stress can negatively impact gut health and lead to increased inflammation. Implementing stress-relief techniques such as regular exercise, mindfulness, journaling, and meditation can help reduce cortisol levels and alleviate IBD symptoms.
Sleep and hydration
Ensuring adequate sleep and hydration are essential for maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals living with IBD. Sleep allows the body to reset and recover, while proper hydration supports digestive functions and helps manage symptoms. Both sleep and hydration are critical components of a holistic approach to IBD management.
Empowering proactive health choices
Empowering individuals with actionable steps towards better gut health is at the heart of this study. By focusing on diet, physical activity, stress management, and sleep, you can take proactive steps to significantly reduce the risk of developing IBD. This knowledge highlights the importance of making informed choices to support long-lasting gut health and overall well-being. Whether you are looking to prevent IBD or manage existing symptoms, small, consistent changes can lead to big improvements. Let’s continue to raise awareness and promote proactive health choices to support those living with IBD.
Sources for this article include:
Submit a correction >>
Tagged Under:
curcumin, digestion, fiber, food cures, grocery cures, gut health, healthy diet, IBD, longevity, nutrients, prevention
This article may contain statements that reflect the opinion of the author